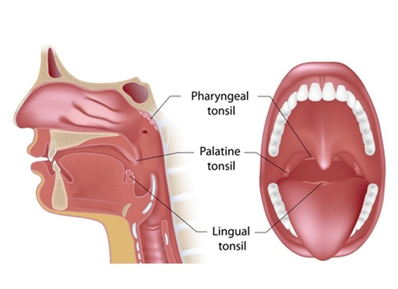
Tonsils
Tonsils are made of soft glandular tissue and are part of the immune system. Tonsils vary in size from person to person. A main function of tonsils is to trap bacteria and viruses (germs) which you may breathe in. Antibodies and immune cells in the tonsils help to kill germs and help to prevent throat and lung infections.
Adenoids
Adenoids are also made of glandular tissue and are part of the immune system. They hang from the upper part of the back of the nasal cavity. Adenoids get bigger after you are born but usually stop growing between the ages of three and five years. Like tonsils, adenoids help to defend the body from infection. They trap bacteria and viruses which you breathe in through your nose. They contain cells and antibodies of the immune system to help prevent throat and lung infections.
Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is an infection of the tonsils. A sore throat is the common symptom. In addition, you may also have a cough, fever, headache, feel sick, feel tired, find swallowing painful, and have swollen neck glands. Pus may appear as white spots on the enlarged tonsils. Symptoms typically get worse over 2-3 days and then gradually go, usually within a week. Most cases of tonsillitis are caused by viruses, some are caused by bacteria.
Do I need my tonsils taken out?
-
If you have frequent and severe bouts of tonsillitis. This usually means:
- Seven or more episodes of tonsillitis in the preceding year, or
- Five or more such episodes in each of the preceding two years, or
- Three or more such episodes in each of the preceding three years.
- The bouts of tonsillitis affect normal functioning. For example, they are severe enough to make you need time off from work or from school. The adenoids may also be removed at the same time for this reason. Throat infections are not totally prevented if the tonsils are removed. However, there is a good chance that their number and severity will be reduced. Many people say they generally feel better in themselves after having their tonsils removed if they previously had frequent bouts of tonsillitis.
- If you have large tonsils that are partially obstructing your airway, this may be a contributing factor to a condition called obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome.
Some problems associated with adenoids
Swollen or enlarged adenoids are common in children. Causes include:- Infections with viruses or bacteria. Once an infection clears, the swelling often goes down but sometimes the adenoids remain enlarged.
- Allergies.
- Often there is no apparent cause.
The adenoids may also be removed at the same time for this reason. Throat infections are not totally prevented if the tonsils are removed. However, there is a good chance that their number and severity will be reduced. Many people say they generally feel better in themselves after having their tonsils removed if they previously had frequent bouts of tonsillitis.
- Breathing through the nose may be noisy. This may get worse and cause difficulty breathing through the nose. The child then mainly mouth breathes.
- A constantly runny nose.
- Snoring at night. In severe cases sleep may be disrupted by the blocked nose and there is difficulty in breathing.
- Swollen adenoids may block the entrance of the Eustachian tube. This is the tube that goes from the back of the nose to the middle ear. It normally allows air to get into the middle ear. If this tube is blocked it may contribute to the formation of glue ear (fluid in the middle ear).
What is the treatment for enlarged adenoids?
In most cases, no treatment is needed. Often the symptoms are mild but may flare up during a cold or throat infection. Adenoids normally gradually shrink in later childhood and usually almost disappear by the teenage years. So symptoms tend to clear in time. If symptoms are severe then a doctor may consider removing the adenoids. For example, if a child regularly has difficulty sleeping or disrupted nights’ sleep due to a blocked nose. Also, some children with glue ear may benefit from removing the adenoids.