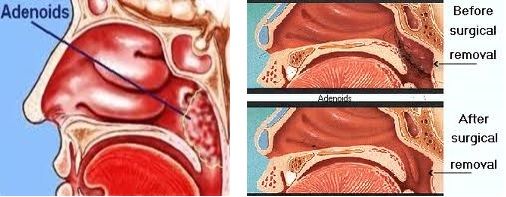
Adenoidectomy is the removal of adenoids. Adenoidectomy is a safe and common throat operation. Swollen or enlarged adenoids are common in children. Causes include:
- Infections with viruses or bacteria. Once an infection clears, the swelling often goes down but sometimes the adenoids remain enlarged.
- Allergies
- Throat infections.
- Recurrent childhood ear disease.
- Often there is no apparent cause.
Common methods of removal include curettage, microdebrider removal and removal with coblator. Bleeding is controlled by thermal sealing of the blood vessels, usually at the same time.
Excision through the mouth
The adenoids are most commonly removed through the mouth after placing an instrument to open the mouth and retract the palate. The adenoids are visualized endoscopically and removed with coblation. This method causes also no bleeding and there is minimal to no post-operative pain.
Excision through the nose
Adenoids may also be removed through the nasal cavity with a surgical suction instrument called a microdebrider endoscopically. With this procedure, bleeding is controlled either with packing or suction cautery. Endoscopic visualization and complete removal is the main advantage of this method.
In rare cases, significant postoperative bleeding may occur. Bleeding usually happens in the first 24 hours after surgery and is short lived. Adenoidectomy is sometimes performed in conjunction with a tonsillectomy.
Return to daily activities when you feel well enough. Some people are ready in a few days; others may need a whole week. It is recommended that children avoid heavy playground activities, physical education class, or sports teams for two weeks.
Report any bleeding immediately. Bleeding usually happens between seven and 10 days after surgery when the wet scabs in the back of the throat are sloughing off. Ninety-eight percent of the time this is a brief bleed that is not significant.
Call your doctor’s office if you experience any of the following:
- A temperature of more than 102°F
- Ear pain that lasts more than three days or severe ear pain
- Neck pain associated with a stiff neck or fixed head position
- Excessive bleeding