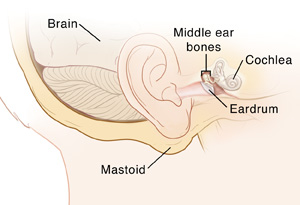
Also known as mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove diseased mastoid air cells from the mastoid bone. It is also used to remove abnormal tissue in the ear known as cholesteatoma. Mastoid exploration or mastoidectomy is usually performed under general anesthesia and it takes around 2 to 3 hours to complete the procedure. There are 3 different types of mastoid exploration procedures, which are done based on the extent of ear diseases.
Cortical Mastoidectomy: Removes infected air cells to improve middle ear ventilation.
Radical Mastoidectomy: An extensive surgery to remove diseased mastoid air cells along with most of the middle ear structures in case of complicated mastoid diseases like ear cancers etc.
Modified Radical Mastoidectomy: A simplified version of radical mastoidectomy, in which infected mastoid air cells and some middle ear structures are removed to treat chronic ear infections or cholesteatoma.
Mastoidectomy helps to clear all the diseased parts of the mastoid bone and reduces the risk of complications such as hearing loss, facial paralysis, brain infections, and affecting the sense of balance.